VPN Services for Privacy are increasingly crucial in today’s digital landscape, where personal data is constantly vulnerable. This guide explores the technology behind VPNs, the privacy concerns they address, and how to choose a reputable service. We’ll delve into the various protocols, security implications, and practical use cases, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of online privacy.
Understanding VPNs is essential for anyone concerned about their online security and privacy. From shielding your data on public Wi-Fi to accessing geo-restricted content, VPNs offer a powerful layer of protection. However, it’s crucial to understand their limitations and choose a provider carefully to ensure you’re getting the best protection possible.
VPN Technology Explained
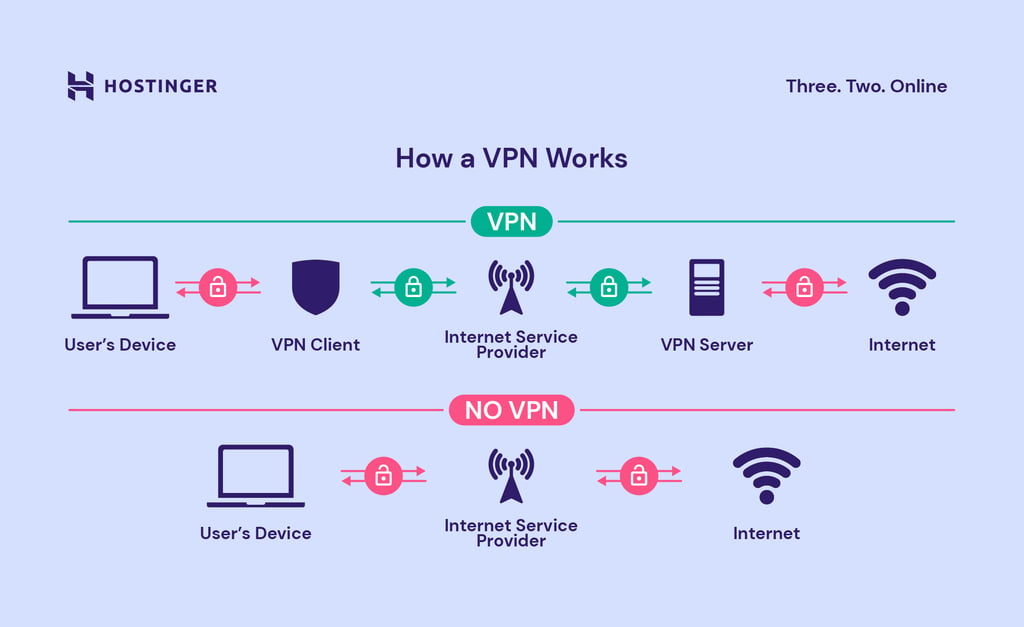
VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, are powerful tools that enhance your online privacy and security. They work by creating an encrypted tunnel between your device and a VPN server, protecting your internet traffic from prying eyes. This ensures your online activities remain confidential, even when using public Wi-Fi networks.
VPNs encrypt internet traffic using cryptographic algorithms. This process essentially scrambles your data, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it. The encrypted data is then sent through the VPN tunnel to the VPN server, where it’s decrypted and forwarded to its intended destination. The process is reversed when data returns to your device.
VPN Protocols
Different VPN protocols offer varying levels of security, speed, and ease of use. Choosing the right protocol depends on your priorities.
Here are some of the most common VPN protocols:
| Protocol | Speed | Security | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| WireGuard | High | High | Easy |
| IKEv2 | High | High | Easy |
| PPTP | High | Low | Easy |
| L2TP/IPSec | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
OpenVPN is an open-source protocol known for its strong security and flexibility. WireGuard is a newer protocol that prioritizes speed and simplicity while maintaining strong security. IKEv2 offers a good balance between speed and security, and is particularly adept at handling connection drops. PPTP is older and faster, but its security is significantly weaker, making it unsuitable for sensitive data. L2TP/IPSec combines the strengths of two protocols, but can be slower than others.
Setting Up a VPN on Different Devices
Setting up a VPN varies slightly depending on your operating system. However, the general process involves downloading the VPN provider’s app or configuring your device’s network settings.
Below is a general outline; specific steps may vary depending on the VPN provider and device model:
Windows
- Download and install the VPN provider’s application.
- Create an account and subscribe to a plan.
- Log in to the application and select a server location.
- Connect to the VPN.
macOS
- Download and install the VPN provider’s application or configure a VPN connection manually through System Preferences.
- Create an account and subscribe to a plan.
- Log in to the application or enter the necessary connection details.
- Connect to the VPN.
iOS
- Download and install the VPN provider’s application from the App Store.
- Create an account and subscribe to a plan.
- Log in to the application and select a server location.
- Connect to the VPN.
Android
- Download and install the VPN provider’s application from the Google Play Store.
- Create an account and subscribe to a plan.
- Log in to the application and select a server location.
- Connect to the VPN.
Remember to always download VPN applications from official app stores to avoid malware.
Privacy Concerns in the Digital Age
The digital age, while offering unprecedented connectivity and convenience, presents significant challenges to individual privacy. Our online activities leave a vast trail of personal data, vulnerable to misuse and exploitation if not adequately protected. Understanding the methods of data collection and the associated risks is crucial for safeguarding personal information.
The sheer volume and variety of personal data collected online is staggering. Websites, apps, and online services routinely gather information through various means, often without explicit user consent or full transparency. This data can include browsing history, search queries, location data, social media interactions, online purchases, and even biometric information. Companies use this data for targeted advertising, market research, and profiling, creating detailed digital profiles of individuals. These profiles can be used to influence purchasing decisions, personalize content, and even predict future behavior.
Data Collection Methods
Websites and apps employ various techniques to collect user data. Cookies track browsing activity across multiple websites. Tracking pixels embedded in emails and websites monitor email opens and clicks. Device identifiers, such as IP addresses and advertising identifiers, link user activity across different devices and platforms. Social media platforms gather vast amounts of personal information through user profiles, posts, and interactions. Many apps request access to a user’s location, contacts, and other sensitive data, often with opaque explanations of how this data will be used.
Risks of Using Public Wi-Fi Without a VPN
Public Wi-Fi networks, while convenient, pose significant security risks. These networks are often unsecured, meaning data transmitted over them is easily intercepted by malicious actors. Without a VPN, your online activity, including passwords, credit card details, and sensitive communications, can be visible to anyone monitoring the network. This makes you vulnerable to data theft, identity theft, and other cybercrimes.
Examples of Real-World Data Breaches
Numerous high-profile data breaches have highlighted the vulnerability of personal information online. The 2017 Equifax breach exposed the personal data of nearly 150 million Americans, including Social Security numbers, birth dates, and addresses. The 2013 Target data breach compromised the credit card information of millions of customers. These breaches resulted in significant financial losses, identity theft, and reputational damage for the affected individuals and organizations. The impact of these breaches underscores the critical need for robust data protection measures.
Data Flow: With and Without a VPN
Data Flow Without a VPN:
“`
User Device –> Unsecured Public Wi-Fi –> Website/Server –> Multiple Intermediaries (Potentially Malicious) –> Website/Server
“`
Data Flow With a VPN:
“`
User Device –> Encrypted Connection (VPN) –> VPN Server –> Website/Server
“`
The visual representation above illustrates the key difference. Without a VPN, your data travels openly across the network, making it vulnerable to interception. With a VPN, your data is encrypted, creating a secure tunnel that protects your information from prying eyes. The VPN server acts as an intermediary, masking your IP address and encrypting your communication.
Choosing a Reputable VPN Service
Selecting a trustworthy VPN provider is crucial for ensuring your online privacy and security. A poorly chosen VPN can expose you to greater risks than having no VPN at all. Understanding the key factors involved in making an informed decision will help you navigate the market and choose a service that truly protects your data.
Choosing the right VPN involves careful consideration of several key aspects. The most important are the provider’s logging policies, its jurisdiction, and the security features it offers. These factors, when evaluated together, determine the level of protection a VPN can provide.
VPN Provider Logging Policies
Understanding a VPN provider’s logging policy is paramount. A truly privacy-focused VPN will have a strict no-logs policy, meaning they do not retain any data about your online activity. This includes your browsing history, IP addresses, or connection timestamps. However, many providers claim “no-logs” but may still collect some metadata, such as connection times or the amount of data transferred. It’s crucial to carefully read their privacy policy to understand exactly what data they collect and for how long they retain it. Transparency is key; a reputable provider will clearly articulate its logging practices. Look for independent audits of their no-logs policy to verify their claims.
Jurisdiction and Data Retention Laws
The jurisdiction under which a VPN provider operates significantly impacts its ability to protect your data. Providers based in countries with strict data retention laws or those with close ties to intelligence agencies may be compelled to share your data with authorities. Choosing a VPN based in a privacy-friendly jurisdiction, such as Switzerland, Iceland, or Panama, often provides a stronger guarantee of privacy. These countries generally have more robust data protection laws and less government surveillance.
VPN Security Features
Beyond logging policies and jurisdiction, the security features offered by a VPN provider are crucial. Look for providers that use strong encryption protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard, which offer robust protection against eavesdropping. Consider whether the provider offers features like a kill switch (which cuts your internet connection if the VPN drops), DNS leak protection (which prevents your real IP address from being revealed), and a split tunneling option (which allows you to route only specific apps through the VPN). A robust suite of security features enhances your overall online protection.
Comparison of VPN Provider Features
Different VPN providers offer varying features and capabilities. Some focus on speed and performance, while others prioritize security and privacy. For example, ExpressVPN is known for its fast speeds and user-friendly interface, but it is more expensive than some competitors. NordVPN, on the other hand, offers a wider range of security features and a larger server network, but its speeds might be slightly slower in some regions. ProtonVPN provides a strong focus on privacy and security, often emphasizing open-source components, but may have a smaller server network compared to larger providers. Ultimately, the best VPN for you will depend on your individual needs and priorities.
Reputable VPN Providers: Pros and Cons
| VPN Provider | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| ExpressVPN | Fast speeds, user-friendly interface, strong security | Expensive |
| NordVPN | Large server network, many security features, good value | Speed can be inconsistent |
| ProtonVPN | Strong focus on privacy, open-source components | Smaller server network |
| Mullvad VPN | Strong privacy focus, simple interface, good value | Limited customer support |
Note: This is not an exhaustive list, and the performance and features of VPN providers can change over time. Always conduct your own research before making a decision.
Red Flags to Watch Out For
Before subscribing to a VPN service, be aware of these potential red flags:
- Unclear or vague privacy policy.
- Lack of transparency about logging practices.
- Overly aggressive marketing claims (e.g., “unbreakable encryption”).
- Negative reviews or complaints from multiple users.
- Unrealistic pricing that is significantly lower than competitors.
- Based in a country with strict data retention laws or known for government surveillance.
VPN Use Cases and Scenarios
VPNs offer a versatile toolkit for enhancing online privacy and security across various digital activities. Their applications extend beyond simply masking your IP address; they provide a crucial layer of protection in numerous scenarios, significantly improving your online safety and anonymity. Let’s explore some key use cases.
Protecting Privacy on Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi hotspots, while convenient, often lack robust security measures. Connecting to these networks without a VPN exposes your data to potential interception by malicious actors. A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and the VPN server, shielding your browsing activity, login credentials, and other sensitive information from prying eyes. For example, if you’re checking your email or online banking at a coffee shop’s free Wi-Fi, a VPN ensures that your data remains private, even if the network itself is insecure. This is because your traffic is encrypted before it leaves your device and decrypted only after it reaches the VPN server.
Accessing Geo-Restricted Content and Streaming Services
Many streaming services and websites offer different content libraries based on geographical location. A VPN allows you to mask your IP address, making it appear as though you are browsing from a different country. This enables access to content that might otherwise be unavailable in your region. For instance, a user in the United States could use a VPN with a server in the United Kingdom to access BBC iPlayer, a streaming service primarily available to UK residents. Similarly, users in countries with restricted internet access can leverage VPNs to bypass censorship and access websites and services blocked by their governments.
Enhancing Online Security for Banking and Shopping
Online banking and shopping involve transmitting sensitive financial information. Using a VPN adds an extra layer of security by encrypting your connection, protecting your data from potential eavesdroppers. This is especially crucial when using public Wi-Fi or unsecured networks. If you’re making an online purchase or accessing your bank account, a VPN helps ensure that your payment details and personal information remain confidential and protected from malicious attacks. This prevents man-in-the-middle attacks, where hackers intercept your data while it’s being transmitted.
Maintaining Online Anonymity
VPNs contribute to online anonymity by masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic. This makes it significantly more difficult for websites, internet service providers (ISPs), and other entities to track your online activities. While a VPN doesn’t guarantee complete anonymity, it adds a considerable layer of privacy, particularly beneficial for individuals concerned about surveillance or tracking. For example, users can utilize VPNs to browse the web without their ISP logging their activity, protecting their browsing history and preferences from third-party observation. However, it’s important to remember that the VPN provider itself will have access to some of your data, so choosing a reputable and trustworthy provider with a strong privacy policy is paramount.
Limitations and Considerations of VPNs
While VPNs offer significant privacy benefits, it’s crucial to understand their limitations. They are not a silver bullet solution for all online security and privacy concerns, and their effectiveness depends on several factors, including the chosen provider and the specific threats faced. Misconceptions about their capabilities can lead to a false sense of security.
VPNs introduce several potential drawbacks that users should be aware of before relying on them for complete online protection. These limitations stem from the inherent nature of VPN technology and the ever-evolving landscape of online threats.
Reduced Internet Speed
Using a VPN can often lead to slower internet speeds compared to a direct connection. This is because your data travels a longer distance, passing through the VPN server before reaching its final destination. Encryption also adds processing overhead, further impacting speed. The extent of the slowdown varies depending on factors like the VPN server’s location, the number of users connected to it, and the VPN provider’s infrastructure. For instance, connecting to a server geographically distant from your location will naturally result in a more noticeable speed reduction than connecting to a nearby server. High-traffic servers can also cause congestion and slower speeds.
Inability to Protect Against All Online Threats
While VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making it difficult for third parties to intercept and monitor your online activities, they do not provide complete protection against all online threats. Malicious software (malware) installed on your device can still monitor your activity even when a VPN is active. Similarly, phishing attacks, which aim to trick users into revealing sensitive information, can succeed regardless of VPN usage, as the core vulnerability lies in user interaction, not network traffic. A VPN secures your connection, but it doesn’t necessarily secure your actions or your device’s security posture.
Legal Implications of VPN Use
The legality of using a VPN varies significantly across different countries. Some countries have strict regulations regarding VPN usage, particularly those with strict censorship or surveillance laws. In such regions, using a VPN might be considered illegal, leading to potential penalties or legal consequences. For example, in some countries, using a VPN to bypass government-imposed internet restrictions is explicitly prohibited. It’s crucial to research the specific laws and regulations of your location and the countries whose servers you intend to use before utilizing a VPN.
Overall Effectiveness of VPNs in Protecting User Privacy
VPNs offer a valuable layer of privacy and security by encrypting internet traffic and masking your IP address, thereby protecting your online activity from unauthorized surveillance and monitoring. However, they are not a panacea for all online threats, and their effectiveness depends on various factors, including the chosen VPN provider, user awareness, and the specific security risks involved. A comprehensive approach to online security that combines VPN usage with other security measures, such as strong passwords, up-to-date antivirus software, and cautious online behavior, is essential for optimal protection.
Wrap-Up
Ultimately, VPN Services for Privacy represent a vital tool in the ongoing battle for online security and freedom. By understanding the technology, selecting a reputable provider, and employing best practices, users can significantly enhance their privacy and control over their personal data. While not a panacea, a well-chosen VPN offers a robust defense against many common online threats, empowering individuals to navigate the digital world with greater confidence.